Kami sebagai konsultan yang juga memiliki jasa membuatkan dashboard report untuk para level tertinggi dalam sebuah pemerintah dan perusahaan swasta, guna memberikan data report dalam bentuk yang diinginkan oleh para owner dan level UP dalam sebuah organisasi untuk kebutuhan kebijakan dan lain sebagainya, dashboard dengan tampilan yang menyenangkan mata, dan tentunya dapat terkoneksi kepada IOT dengan sistem perhitungan real time. silahkan berkonsultansi melalu url di bawah ini:
Friday, September 1, 2023
Grafana Dashboard Report
Saturday, April 15, 2023
Menulis blog dengan AI
Tentu saja, Anda dapat menggunakan teknologi AI untuk menulis blog. Ada beberapa platform seperti Copy.ai dan Articoolo yang memungkinkan Anda untuk menghasilkan konten blog dengan cepat menggunakan teknologi AI.
Namun, perlu diingat bahwa meskipun teknologi AI dapat membantu Anda dalam membuat bahan tulisan, Anda masih perlu meluangkan waktu untuk melakukan penelitian dan mengembangkan ide yang tepat untuk konten yang ingin Anda buat. Selain itu, Anda juga harus memeriksa kualitas konten yang dihasilkan oleh AI untuk memastikan bahwa konten tersebut sesuai dengan standar kualitas yang Anda inginkan.
Jadi, menggunakan teknologi AI untuk menulis blog dapat menjadi alat yang berguna dalam meningkatkan efisiensi dalam penulisan, tetapi perlu diimbangi dengan kualitas dan keaslian konten yang dihasilkan.
Ada beberapa cara yang dapat Anda lakukan untuk membuat tulisan blog menggunakan teknologi AI. Di bawah ini adalah beberapa langkah yang dapat Anda ikuti:
Pilih platform AI yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda. Ada beberapa platform AI yang dapat digunakan untuk membuat konten blog, seperti Copy.ai dan Articoolo. Pastikan untuk memilih platform yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda dan memiliki fitur yang Anda butuhkan.
Tentukan topik dan jenis konten yang ingin Anda buat. Sebelum memulai, pastikan untuk menentukan topik dan jenis konten yang ingin Anda buat. Ini akan membantu AI dalam membuat konten yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda.
Masukkan instruksi dan keyword yang relevan. Platform AI biasanya membutuhkan instruksi dan keyword yang relevan untuk memahami apa yang ingin Anda tulis. Pastikan untuk memberikan instruksi yang jelas dan keyword yang tepat.
Tunggu AI menghasilkan konten. Setelah memberikan instruksi dan keyword, platform AI akan memproses informasi tersebut dan menghasilkan konten yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda. Pastikan untuk memeriksa kualitas dan keaslian konten yang dihasilkan sebelum mempublikasikannya.
Edit dan revisi konten. Meskipun AI dapat membantu Anda dalam membuat konten, masih perlu dilakukan pengeditan dan revisi untuk memastikan bahwa konten tersebut sesuai dengan standar kualitas yang Anda inginkan. Pastikan untuk melakukan pengeditan dan revisi sebelum mempublikasikan konten tersebut.
Jadi, itulah beberapa cara untuk membuat tulisan blog menggunakan teknologi AI. Pastikan untuk memilih platform AI yang tepat, memberikan instruksi yang jelas, dan melakukan pengeditan dan revisi untuk memastikan kualitas konten yang baik.
Thursday, March 30, 2023
Cara perpanjang sertifikat elektronik kadaluarsa
Saturday, February 18, 2023
Cara menghapus watermark word di Macbook
Pilih Desain > Marka Air. (Di Word untuk Mac 2011, pilih Tata Letak Halaman > Marka Air).
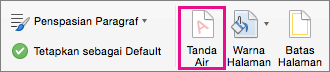
Di kotak Sisipkan Cap Air, pilih Tanpa cap air.
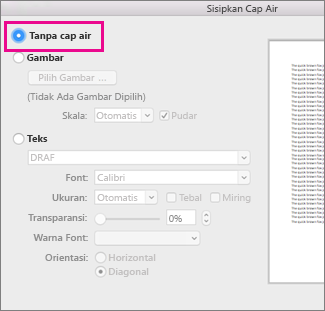
Hapus marka air dengan mengklik area header
Jika tidak dapat menghapus marka air menggunakan Hapus Marka Air, cobalah cara ini:
Klik ganda di dekat bagian atas halaman untuk membuka area header.

Klik marka air untuk memilihnya.
Tekan tombol Hapus pada keyboard.
Wednesday, January 11, 2023
Cara Mengaktifkan USB Debugging Xiaomi 4A
Dalam melakukan beberapa hal di perangkat Android, misalnya memasang custom recovery dan rooting, kadang-kadang Anda membutuhkan mode debugging dari perangkat android.
Mode ini sebenarnya adalah metode yang dipakai oleh programer atau pengembang perangkat lunak, untuk mencari error dari aplikasi yang dikembangkan, dengan menganalisis alur kerjanya.
Namun dengan kemampuannya tersebut, mode ini dapat dimanfaatkan oleh pemakai perangkat Android untuk mengakses beberapa hal di perangkat Android milik Anda melalui perangkat komputer atau laptop.
Di perangkat Android kamu bisa mengaktifkan mode ini, dengan mengaktifkan mode developer di perangkat yang kamu miliki. Di perangkat Xiaomi, Kalian dapat mengaktifkannya dengan cara berikut ini:
A. Cara Menggunakan Mode Developer Perangkat Xiaomi
1. Anda dapat membuka settings melalui perangkat Xiaomi yang Anda miliki.
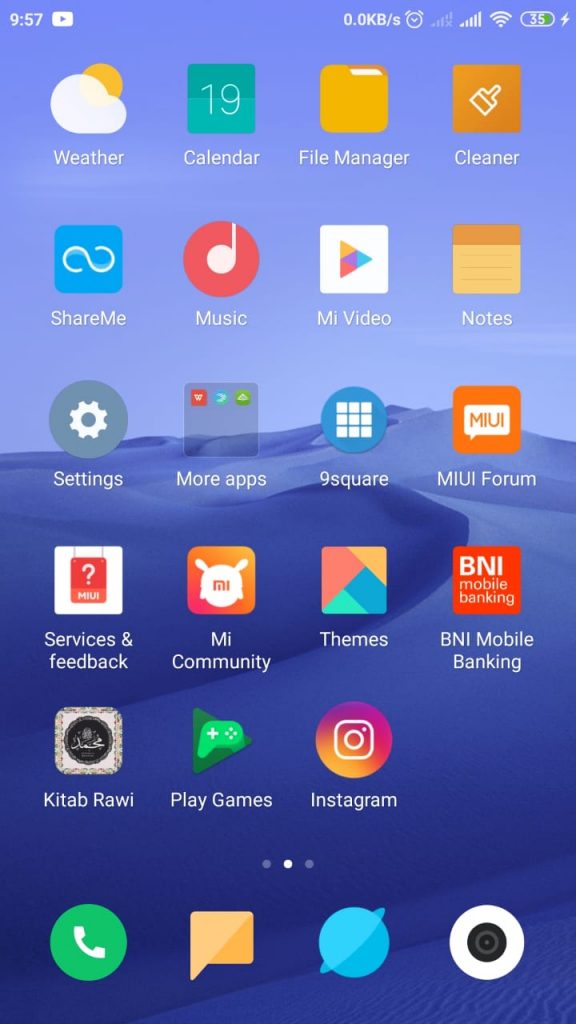
2. Setelah itu, gulir ke bawah dan pilih About Phone.
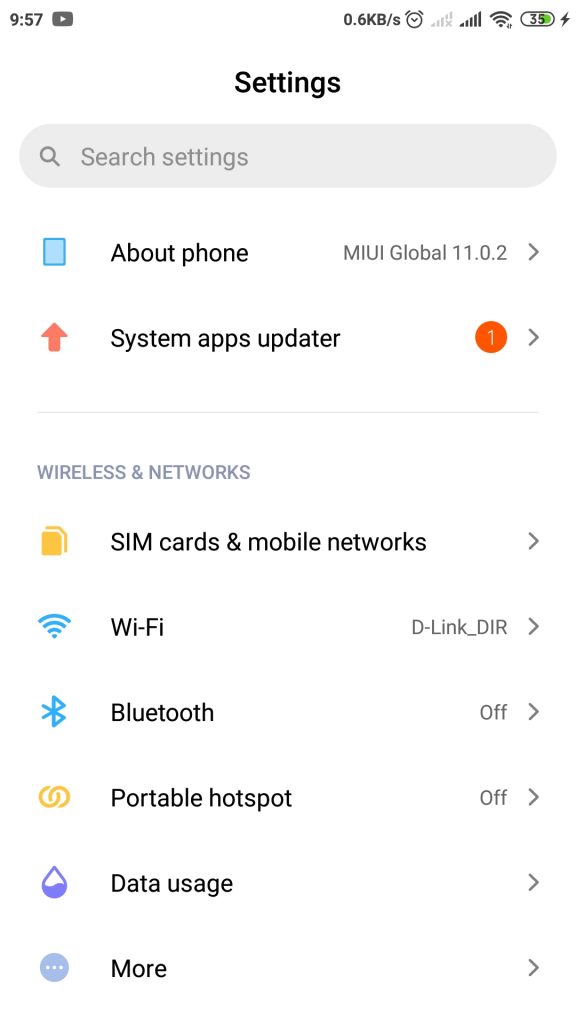
3. Lalu di halaman tersebut, kemudian ketuk MIUI Version berulang-ulang dengan selama 7 kali, sampai muncul tulisan yang mengindikasikan bahwa mode pengembang telah diaktifkan.

Apabila sudah sukses, Anda sekarang dapat mengaktifkan pilihan USB Debugging di perangkat Xiaomi yang akan kalian pakai. Untuk melakukannya kamu bisa membuka halaman developer yang telah diaktifkan. Secara lebih rinci Anda bisa mengikuti langkah-langkah berikut ini.
B. Cara Mengaktifkan USB Debugging di Pengaturan Developer Perangkat Xiaomi
1. Kalian bisa membuka pengaturan kembali.
2. Setelah itu cari dan pilih opsi Additional Settings yang ditampilkan pada layar tersebut.
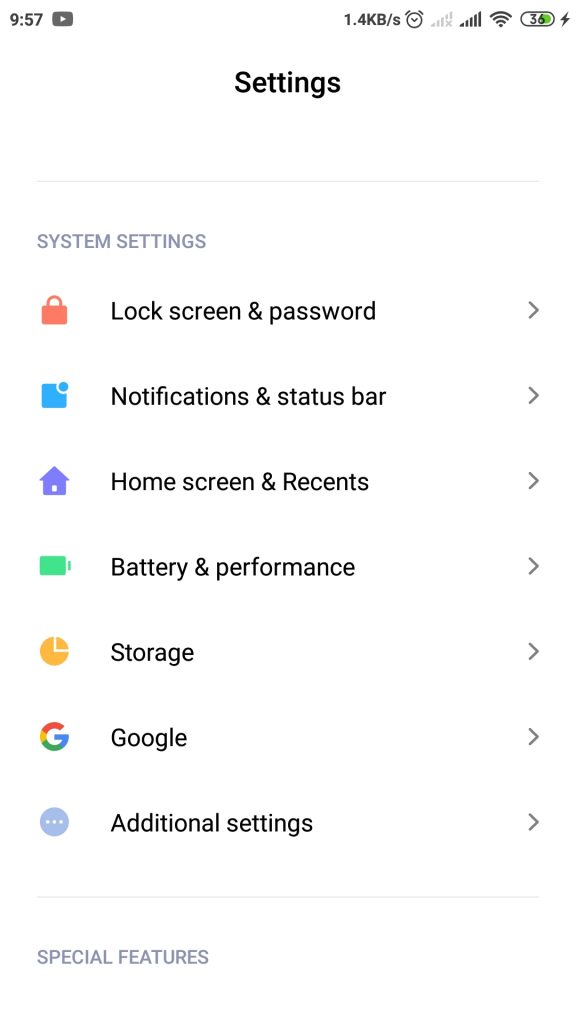
3. Selanjutnya, gulir ke bawah pada halaman Additional Settings, cari pilihan Developer Options.
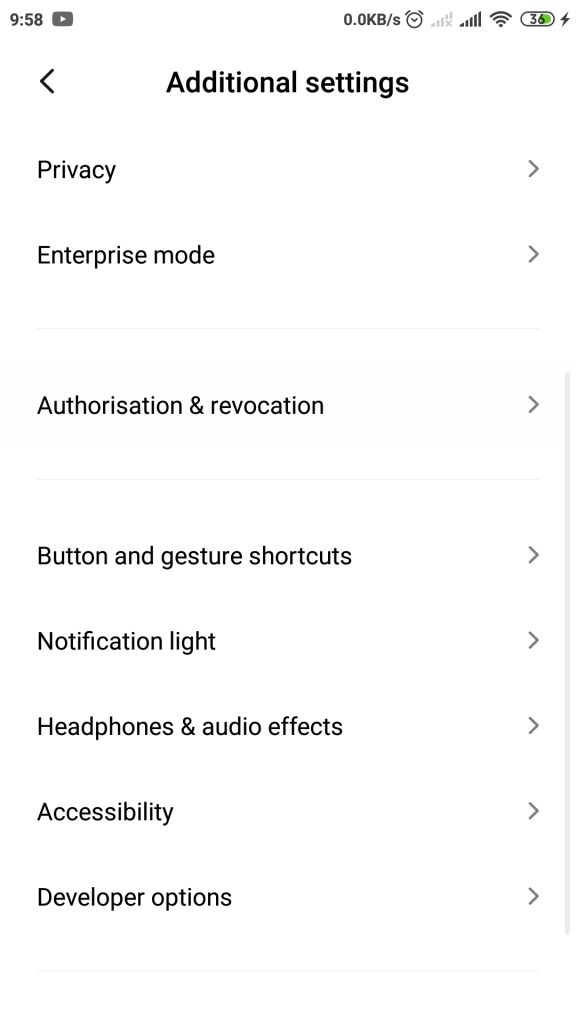
4. Apabila, jika pilihan developer tersebut belum tampil, berarti kalian harus mengulangi langkah-langkah cara mengaktifkannya di poin A.
5. Buka pilihan tersebut, kemudian cari dan tekan pilihan USB Debugging hingga tombol slider ke posisi hidup.
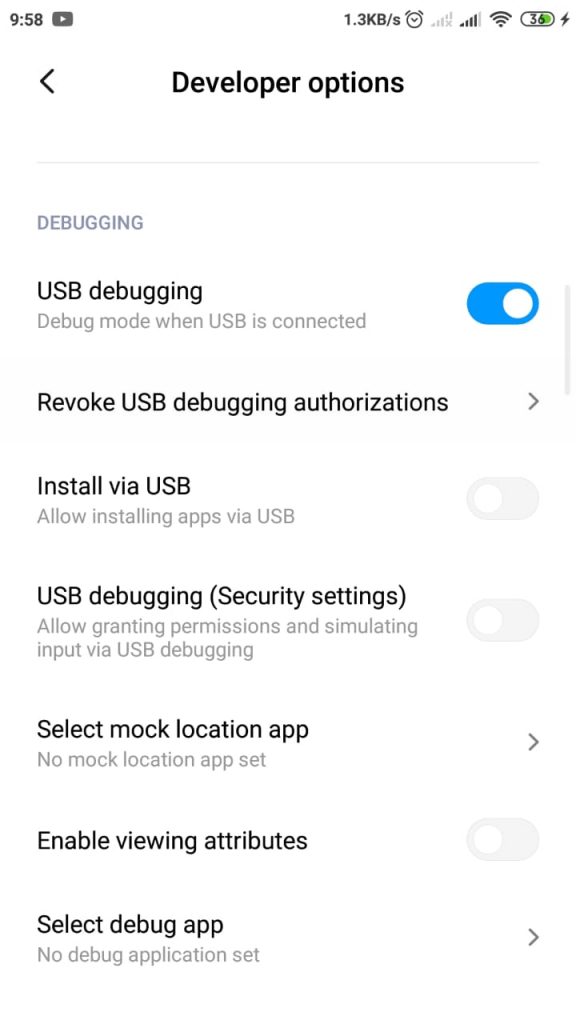
Jadi, dengan menyalakan opsi USB Debugging tersebut, perangkat Xiaomi yang kamu punya sekarang akan masuk ke mode debugging-nya secara otomatis setiap kali terhubung dengan perangkat komputer atau laptop.
Dan itulah dia artikel yang membahas mengenai bagaimana cara mengaktifkan usb debugging pada perangkat xiaomi.
Sumber: https://irvama.com/cara-mengaktifkan-usb-debugging-xiaomi-4a-irvama-com/















